|
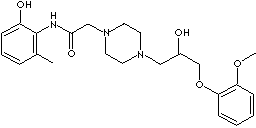
RANOLAZINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE |
|
N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-4-(2-hydroxy-3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)propyl)-1-piperazineacetamidedihydrochloride; (±) -4-(2-Hydroxy-3-(o-methoxyphenoxy)propyl)-1-piperazineaceto-2',6'-xylididedihydrochloride; (+-)-4-(2-Hydroxy-3-(o-methoxyphenoxy)propyl)-1-piperazineaceto-2',6'-xylidide dihydrochloride; (+-)-N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-4-(2-hydroxy-3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)propyl)-1-piperazineacetamide dihydrochloride; Ranexa; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
95635-55-5 (parent); 95635-56-6, 94386-66-0, 110445-25-5 (dihydrochloride); |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C24H33N3O4·2HCl |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
500.46 |
|
CHEMICAL FAMILY |
|
| RELATED CATEGORIES | Anti-anginal agent |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
white to off-white crystalline powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
117 - 122 C ( parent); 222 - 229 C (dihydrochloride) |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
soluble (10 mg/ml) |
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong acids, Strong bases |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
NOx, COx, Hydrogen chloride gas |
| POLYMERIZATION |
Will not occur. |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2. Flammability: 1, Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
This substance is not classified as dangerous |
|
EYE |
May cause eye irritation. In case of eye contact, flush eyes with water as a precaution. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through skin. May cause skin irritation. In case of skin contact, wash off with soap and plenty of water. |
|
INGESTION |
May be harmful if swallowed. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Rinse mouth with water. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. If breathed in, move person into fresh air. If not breathing give artificial respiration. |
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
|
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ranolazine Ranolazine is a potential anti-anginal agent that acts by shifting ATP production away from fatty acid oxidation in favor of glucose oxidation. Because more oxygen is needed to phosphorylate a given amount of ATP during fatty acid oxidation than during carbohydrate oxidation, the ranolazine-induced shift in substrate utilization reduces oxygen demand without decreasing the ability of the tissue to do work.In three placebo controlled studies in angina patients, an immediate release (IR) formulation of ranolazine increased treadmill exercise parameters without associated changes in rest or exercise heart rates or decreases in rest or exercise blood pressures. Statistically significant increases in exercise times were only observed, however, after doses of > 240 mg, when ranolazine plasma concentrations were near their peak. There was no evidence for anti-anginal efficacy 8 or 12 hours after any dose. These studies suggested potential for ranolazine as an anti-anginal drug but indicated that the immediate release formulation was impractical because of the short duration of its effect. They did, however, provide information concerning ranolazine plasma concentrations necessary for an anti-anginal effect. Based on these results, a sustained release (SR) formulation of ranolazine was developed. Another study has shown that subjects treated concomitantly with ranolazine and diltiazem allows the higher ranolazine plasma levels to occur. Both ranolazine SR and IR appear to be safe and well tolerated in short-term, solid blind, placebo controlled trials which have included over 1400 patients, most of whom had stable angina. (http://www.angiogenesis-center.org/)In the current, pilot study, researchers found that a drug, ranolazine (brand name Ranexa, CV Therapeutics) shortens the QT interval by about 5 percent; just enough to reduce symptoms and risks associated with one form of LQTS (LQT3-deltaKPQ). It is one of three forms of the disease that together make up 90 percent of LQTS cases. Past studies have shown that patients with angina, severe chest pain caused by inadequate blood flow to the heart, are also more likely to experience arrhythmias. Researchers got a clue that ranolazine, approved in January 2006, might influence QTc during its angina clinical trials, where it was found to have electrophysiological side effects.( http://www.news-medical.net/) The mechanism of action of ranolazine is unknown. It does not increase the rate-pressure product, a measure of myocardial work, at maximal exercise. In vitro studies suggest that ranolazine is a P-gp inhibitor. Ranolazine is believed to have its effects via altering the trans-cellular late sodium current. It is by altering the intracellular sodium level that ranolazine affects the sodium-dependent calcium channels during myocardial ischemia. Thus, ranolazine indirectly prevents the calcium overload that causes cardiac ischemia. (http://www.drugbank.ca/cgi-bin/)
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white crystalline powder |
|
CONTENT |
98.0% min |
| RELATED SUBSTANCES |
Individual impurity:
0.5% max Total impurity: 1.0% max |
| RESIDUE ON IGNITION |
0.2% max |
|
HEAVY METALS |
20ppm max |
| LOSS ON DRYING | 1.0% max |
|
|
| PRICE |
|
|